April 11th is highlighted in medical calendar as Parkinson’s Disease Awareness Day:
an occasion to talk about parkinsonism, its diagnosis and modern methods of treatment.
The video from news.am refers to neurosurgical treatment of parkinsonism at "Arabkir" Medical Center emphasizing how effective deep brain stimulation with neuromonitoring can be and how important it is for improving the quality of human life.
-
The 60-year-old man has had Parkinson's disease for over 10 years. He had been receiving drug treatment for many years, but the medications are no longer helpful, and even cause some complications. According to neurologist Zaruhi Tavadyan in a conversation with NEWS.am Medicine, the man had problems with work, social activities, and quality of life. The doctors at “Arabkir” Medical Center suggested a surgical treatment method - deep brain stimulation, which will allow him to return to his active life.
“Parkinson’s disease is a chronic progressive neurological disorder of the central nervous system. Its classic symptoms are mainly motor: slowness in motion, tremor, impaired gait, coordination problems, muscle stiffness, and many non-motor symptoms like depression, sleep disorders, pain, etc. All of these symptoms together have a significant impact on the quality of life.
During this disorder and drug treatment, patients may experience complications related to the treatment, irregular response to medications, irregular movements. At a certain point, it becomes difficult for patients to continue their treatment with conventional medications alone” says Zaruhi Tavadyan. She also mentions that deep brain stimulation has been used as a treatment method for over two decades. It allows for continuous adjustments in the patient’s mobility over time and helps them to remain active. Deep brain stimulation is a surgery, during which electrodes are placed in specific areas of the brain, which are then connected to a stimulation device implanted under the skin in the chest cavity. The device generates electrical impulses that inhibit abnormal brain activity. This is a complex operation, and surgeons need to find the correct position of electrodes without damaging the motor area of the brain. In the past, the surgery was performed with local anesthesia as the patient had to perform some tasks during the operation in order to evaluate the method's effectiveness and safety. For example, violinist Roger Frisch is known to have played the violin during this type of operation. Today, in “Arabkir” Medical Center, deep brain stimulation is performed with modern technology, neuromonitoring, and there is no longer a need to keep the patient awake, says neurosurgeon Sevak Badalyan.
“In our center, deep brain stimulation is performed under general anesthesia and under the control of neuromonitoring, which has many advantages. Firstly, the patient is in a more comfortable state under general anesthesia, and neuromonitoring allows us to adjust the electrode's position and avoid possible side effects of stimulation. Neuromonitoring is a widely used method nowadays. It involves closing an electrical circuit, i.e . a stimulation of the corresponding area is done and the stimulus is recorded from the peripheral muscles. In other words, it can be facial muscle, upper or lower limbs, therefore, it will be facial nerve or hypoglossal nerve, depending on the specifics of the operated region. The goal is to avoid the damage to relevant areas and pathways” he says.
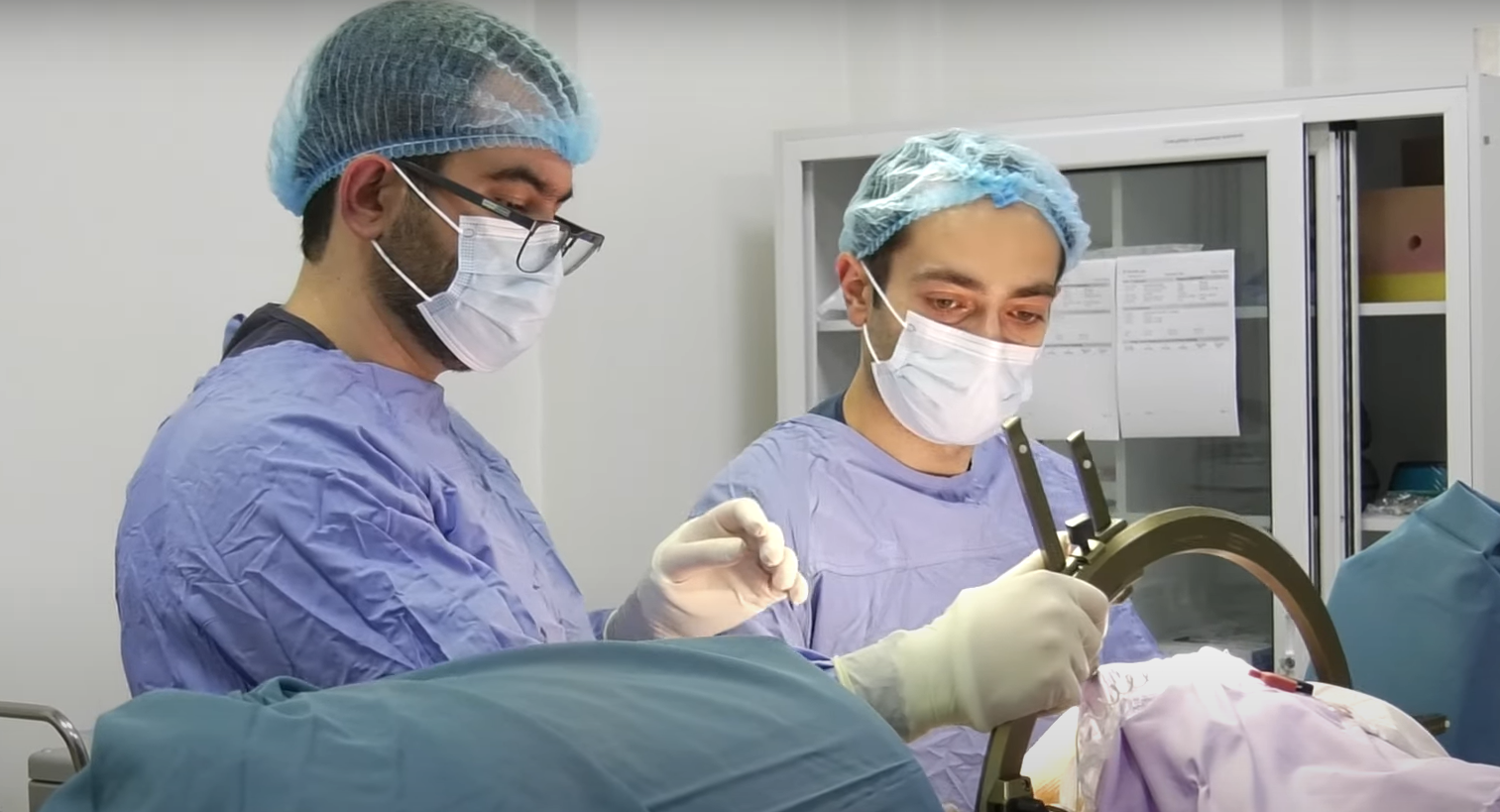
Before the operation, doctors carefully study the patient's brain MRI image, find target nuclei and insert electrodes virtually. Then, right before the operation, contrast CT-scan is performed, the results of which are then combined with MRI. To determine the precise place of where electrodes should be placed, a special coordinate system called stereoscopic circle, is used, Niko Arzumanyan, the head of the Neurosurgery Service has noted.
“The intervention consists of several stages. In the first stage of the operation, a special metal device is attached to the patient’s head, which helps us to create a virtual coordinate system, and by combining the results of the computed tomography and MRI imaging through the appropriate program, we are able to get coordinates we need, and with the corresponding coordinates, insert the electrodes in the right place with an accuracy of up to 0.6mm” he says.
Niko Arzumanyan mentions that deep brain stimulation has been used in “Arabkir” Medical Center for over a year now, and all the operated patients are satisfied with the results. All of this became possible thanks to the latest equipment and digital technologies acquired by the center.
Deep brain stimulation is used not only to treat parkinsonism, but for other neurological and even psychiatric disorders as well, says Zaruhi Tavadyan.
“Deep brain stimulation is used primarily for Parkinson’s disease, as well as for genetic or essential tremor, and in pediatrics for some types of dystonia. By now, the indications for deep brain stimulation are increasing, the field is expanding, and in the future this method will be used for movement disorders as well, and not only. For example, it can be used in psychiatry, but for now it is used for movement disorders such as classical parkinsonism, essential tremor and dystonia”, she says.
3-4 weeks after the surgery, when the patient’s wounds have healed, the doctors will run the stimulator and make the adjustments. As a result, the patient's slowness of movement, tremor, gait and speech will be corrected, the use of medication will be reduced, which will significantly improve his quality of life.